Also, I found interesting that Monte-Carlo simulations run at the Los Alamos National Laboratory relied on a relatively simple linear congruential generator (LCG) producing 24- or 48-bits integers for at least 40 years. LCGs are today touted as some of the worst random number generators, exhibiting strong patterns in 2D projections. Also the period chosen was very small by today’s standards: 7E13.
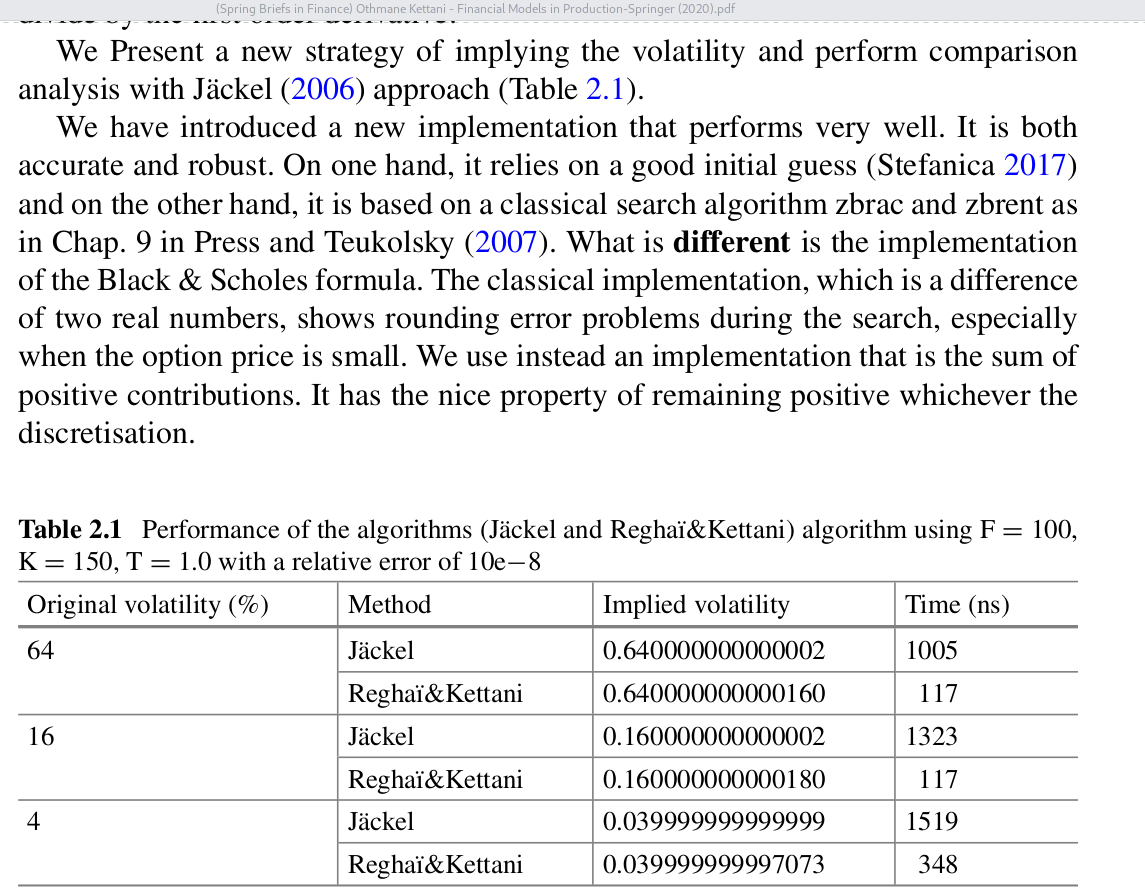
Regarding the integer to floating point numbers conversion, I remember somewhere reading someone arguing to generate numbers also close to 0 (with appropriate distribution) while most implementations just generate up to \(2^{-32}\) or \(2^{-53}\) (the latter being the machine epsilon).
I see one major issue with the idea: if you stumble upon a tiny number (perhaps you’re unlucky) like \(10^{-100}\), then it may distort significantly your result (for example if you call the inverse cumulative normal to generate normal numbers and calculate the mean), because your sample size may not be not large enough to compensate. Perhaps for the same kind of reason, it may be better to use only 32 bits (or less bits). The consequence is that tail events are bound to be underestimated by computers. In a way this is similar to Sobol, which generates with a precision of \(2^{-L}\), for \(2^{L} - 1\) samples.
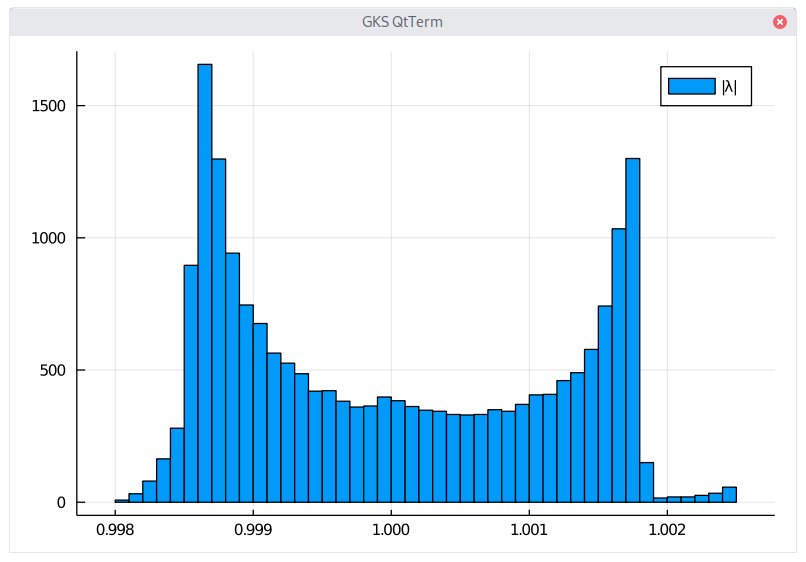
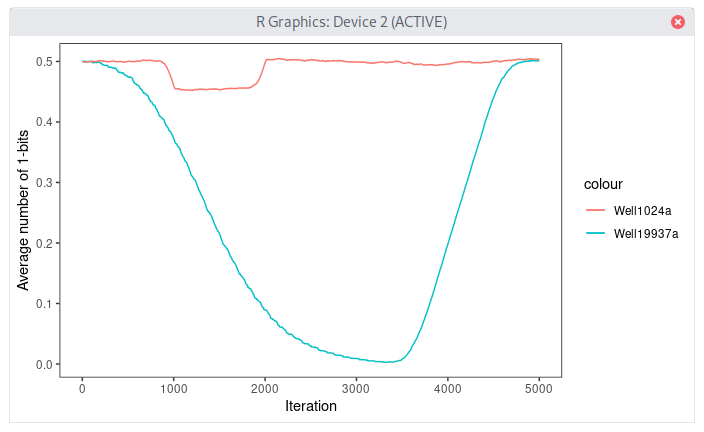
Finally, some personal tests convinced me that a very long period, such as the one in MT, may not be a good idea, as, in the case of MT, the generator is then slower to recover from a bad state. For Well19337a, it may take 5000 numbers and the excess-0 state is very pronounced (period of \(2^{19937}-1\)). While this is way better than the old MersenneTwister (the newer dSFMT is also much better, around twice slower than Well19937a in terms of recovery), which requires more than 700 000 numbers to recover from the bad state, it may still be problematic in some cases. For example, if you are particularly unlucky, and pick a bad choice of initial state (which may actually have good properties in terms of number of 0 bits and 1 bits) and your simulation is of small size (16K o even 64K numbers), there may be visible an impact of this excess-0 state on the simulation results.
For Well1024a (period of \(2^{1024}-1\)), full bit balance recovery takes around 500 numbers and the excess-0 state is much much milder so as to be a non-issue really.
Below is an example of (manufactured) bad seed for Well19937a, which will lead to excess-0 state after ~1000 numbers, and lasts ~3000 numbers.
int[] seed = { 1097019443, 321950666, -1456208324, -695055366, -776027098, 1991742627, 1792927970, 1868278530,
456439811, 85545192, -1102958393, 1274926688, 876782718, -775511822, 1563069059, 1325885775, 1463966395,
2088490152, 382793542, -2132079651, 1612448076, -1831549496, 1925428027, 2056711268, 108350926,
1369323267, 149925491, 1803650776, 614382824, 2065025020, 1307415488, -535412012, -1628604277,
1678678293, -516020113, -1021845340, -793066208, -802524305, -921860953, -1163555006, -1922239490,
1767557906, -759319941, -245934768, 939732201, -455619338, 1110635951, -86428700, 1534787893,
-283404203, 227231030, -313408533, 556636489, -673801666, 710168442, 870157845, 1109322330, -1059935576,
-513162043, 1192536003, -1602508674, 1246446862, 1913473951, 1960859271, 782284340, 122481381,
-562235323, 202010478, -221077141, -1910492242, -138670306, -2038651468, 664298925, -156597975,
-48624791, 1658298950, 802966298, -85599391, -406693042, 1340575258, 1456716829, -1747179769,
1499970781, 1626803166, -687792918, -1283063527, 733224784, 193833403, -230689121, 775703471, 808035556,
337484408, -518187168, -2136806959, -2115195080, -2137532162, 873637610, 216187601, -477469664,
-1324444679, 1339595692, 378607523, 2100214039, 701299050, -178243691, 1858430939, 1595015688,
2139167840, 500034546, -1316251830, 1619225544, 1075598309, 1300570196, -327879940, 414752857,
-145852840, -1287095704, 355046097, 886719800, -20251033, 1202484569, -96793140, 1846043325, 1192691985,
928549445, 2049152139, -1431689398, 348315869, -1582112142, -1867019110, 808920631, -342499619,
-1714951676, 279967346, 385626112, 416794895, -578394455, -1827493006, -2020649044, -396940876,
937037281, -385129309, -1905687689, -526697401, -1362989274, 1111153207, 27104439, 115923124,
-1759234934, 495392989, 1848408810, 655641704, 1484391560, 128171526, -91609018, 647891731, 1451120112,
882107541, 1391795234, -1635408453, 936540423, 564583769, 379407298, -1829214977, 1416544842, 81232193,
-936231221, 1193495035, 1076101894, 860381190, 728390389, -511922164, -1588243268, -142612440,
1018644290, 292363137, 475075683, -2071023028, -1224051451, -891502122, 1575411974, -123928662,
1080946339, 962151951, -1309758596, -558497752, -2126110624, -73575762, -2078269964, -676979806,
-1165971705, 557833742, -828399554, -1023609625, -482198028, 1700021748, 25284256, -826748852,
-2139877059, -1280388862, -1521749976, 738911852, -1676794665, -1595369910, -748407377, -709662760,
680897802, 2094081, -1889225549, -1101409768, -1620191266, 506408464, 1833777989, 244154307,
-1406840497, -860371799, 1337820797, 614831742, 1965416365, 2044401180, -459642558, -339576217,
-1599807697, -689958382, 1544444702, 872938368, 871179645, -957732397, 958439335, -770544793,
-1363785888, -1484683703, 2021823060, -1871739595, -1355536561, -926333946, -1552155978, -171673777,
993986110, -727417527, 1065139863, 517970706, -453434939, -424362471, 1823459056, -48408572, 863024600,
190046576, 90264753, 1667010014, -529079929, -1269908431, -2073435303, -1123302722, -1986096205,
-173411290, -693808986, -1618071944, 990740121, 2120678917, -203702980, -1186456799, -776433190,
172239859, 126482680, 2048550654, 266718714, 913094204, -937686511, -2096719726, 627687384, 533376951,
-1413352057, 1900628390, -244457985, 896712029, -1232645079, 1109406070, 1857772786, 86662738,
-488754308, 360849611, 1187200060, -341213227, 1705204161, -121052077, 1122608367, 2118749875,
243072462, 204425155, 1386222650, 2037519370, 93424131, -785650065, 45913153, -448515509, -1312863705,
-834086187, -2101474931, 1478985081, 1288703145, -1705562554, -1758416930, 1440392126, 1783362885,
279032867, -610479214, 223124643, -367215836, 2140908029, -780932174, 581404379, -1741002899,
2035577655, -1060511248, 1765488586, -380048770, 1175692479, -1645645388, 1865881815, 2052353285,
-492798850, -1250604575, -2077294162, 1768141964, 1457680051, -141958370, -1333097647, -285257998,
-2063867587, 1338868565, -304572592, -1272025276, 1687010269, -1301492878, -931017010, -1303123181,
-1963883357, 1920647644, 2009096326, 2094563567, 1137063943, -1003295201, -382759268, 1879016739,
-153929025, -1008981939, -646846913, 1209637755, 1560292706, 725377476, -1457854811, 264360697,
-197926409, -908579207, -894726681, 194950082, -1631939812, 1620763228, -659722026, 208285727,
1389336301, -1900616308, 1690406628, 1688632068, -717888847, -1202067733, -2039964596, 1885630763,
475497380, -488949843, -1679189364, -1358405375, 2132723, -1164703873, -1727721852, 1747612544,
-885752188, -1450470713, 791640674, 996275741, 397386006, -1977069145, -1841011156, -431458913,
47865163, 1200765705, 1962743423, 1933688124, -1165500082, -1969953200, 597796878, 1379082884,
-737292673, 1776141019, 1882257528, -991388501, -1357999809, 497686068, 314237824, -882469634,
2142408833, -1624234776, -292985482, -412114618, 380982413, -1351123340, 1799246791, 491394003,
496521378, 1074735076, 1131599274, -1379708840, -256028322, 118705543, 58715272, -449189848, 35299724,
-1440805390, -893785929, 217256482, 640658194, -1786418454, 1111743603, -2027083091, 2022760758,
-1001437881, -202791246, 636755388, 1243592208, 1858140407, 1909306942, 1350401794, 188044116,
1740393120, -2013242769, 207311671, 1861876658, -962016288, -865105271, -15675046, -1273011788, 9226838,
906253170, -1561651292, -300491515, -409022139, 611623625, 1529503331, 943193131, -1180448561, 88712879,
1630557185, -17136268, -1208615326, 428239158, 256807260, -918201512, 2022301052, -1365374556,
-877812100, 2029921285, -1949144213, 2053000545, -563019122, 224422509, 741141734, -1881066890,
-280201419, 1959981692, 302762817, 477313942, 358330821, -1944532523, -980437107, -1520441951,
-613267979, -1540746690, -1180123782, -1604767026, 1407644227, -926603589, 1418723393, 2045743273,
-309117167, 949946922, -105868551, -487483019, 1715251004, -221593655, 2116115055, -1676820052,
394918360, -2111378352, 1723004967, -224939951, -730823623, -200901038, -2133041681, 1627616686,
-637758336, -1423029387, 1400407571, 861573924, 1521965068, -614045374, 412378545, 2056842579,
-225546161, 1660341981, 1707828405, -513776239, -115981255, -1996145379, -2009573356, 44694054,
616913659, 1268484348, -980797111, -464314672, 1545467677, 174095876, -1260470858, 1508450002,
1730695676, -613360716, 2086321364, -144957473, 202989102, 54793305, -1011767525, 2017450362,
-761618523, 1572980186, -138358580, 1111304359, 1367056877, 1231098679, 2088262724, 1767697297,
-921727838, 1743091870, 974339502, 1512597341, -1908845304, 1632152668, -987957372, 1394083911,
433477830, 579364091, -27455347, -772772319, -478108249, 641973067, -1629332352, 1599105133, 1191519125,
862581799, -850973024, -188136014, -398642147, 513836556, 1899961764, 2110036944, 512068782,
-1988800041, -2054857386, 321551840, -1717823978, -1311127543, 373759091, 71650043, 565005405,
1033674609, 1344695234, 709315126, 1711256293, -1226183001, -1451283945, 628494029, 1635747262,
-689919247, 1091991202, 1283978365, 749078685, 1987661236, 1992010052, -2003794364, 2099683431,
267011343, -1326783466, 678839392, -312043613, 1565061780, 178873340, -719911279, -314555472,
-231514590, 161027711, 1080368165, 1660461722, -337050383, 399572447, -1555785489, -1502682588,
2143158964, 592925741, -980213649, -724779906, 395465301, 635561967, 700445106, 1198493979, 1707436053,
149364933, -1767142986, 1950272542, -819076405, 687992680, 1960992977, 1342528780, -2110840904,
340172712, -486861654 };